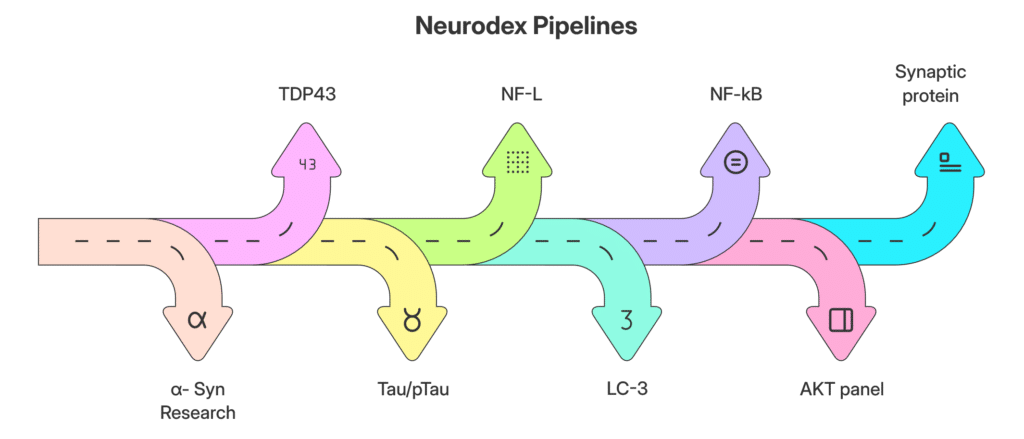
Biomarker Pipeline
Neurodex biomarker pipeline
α-Syn
Discovery
Analitical Validation
Clinical Validation
TDP43
Discovery
Analytical Validation
Clinical Validation
Tau/pTau
Discovery
Analytical Validation
Clinical Validation
NF-L
Discovery
Analytical Validation
Clinical Validation
LC-3
Discovery
Analytical Validation
Clinical Validation
NF-kB
Discovery
Analytical Validation
Clinical Validation
AKT panel
Discovery
Analytical Validation
Clinical Validation
Synaptic protein
Discovery
Analytical Validation
Clinical Validation
I think one of the important things that isn't a a requirement for us to work with the CRO, but definitely sets some CROs apart from others, is that we feel like we are actually collaborating with them. We are both working on a project. We're not just telling them, hey, do this and they're doing it. We feel like we're collaborating with them.
NeuroDex Client
Great communication. They're responsive right away.
NeuroDex Client
I think Neurodex and their collaborators at NIH and other research institutes and universities could be key in the proof of concept that NDEs are indeed a very important tool, can be a very important tool in synaptic neuron disease research.
NeuroDex Client
I think my preference would be to do NDE work with NeuroDEX because they have done so much of it that I would trust them.
NeuroDex Client
Sometimes it's very hard to get a pure sample of extracellular vesicles. You can pick up other white blood cells and things of that sort. But one of the reasons we're working with NeuroDex is that we feel like they have perfected this method as opposed to everyone else. So that's why we're taking a shot with them at this.
NeuroDex Client
In this section, we will explore the role of α-Synuclein (α-Syn) in neurodegenerative diseases. α-Syn is a presynaptic protein that is critical for synaptic function. Studies have shown that abnormal aggregation of α-Syn is a hallmark of Parkinson’s disease and other synucleinopathies. For instance, the formation of Lewy bodies, which are intracellular aggregates of α-Syn, is a key pathological feature observed in patients with these disorders. Recent research also suggests that the presence of α-Syn in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) may serve as a potential biomarker for early diagnosis. This indicates the importance of monitoring α-Syn levels in individuals with risk factors for neurodegenerative diseases.
This holistic approach provided by the Neurodex biomarker pipeline can lead to breakthroughs in early detection and treatment.
By utilizing the Neurodex biomarker pipeline, we can understand the complex interactions of biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases.
The Neurodex biomarker pipeline is essential for understanding the implications of α-Synuclein levels in neurodegenerative diseases. By integrating the Neurodex biomarker pipeline into clinical practices, healthcare professionals can enhance early diagnostics.
Incorporating the Neurodex biomarker pipeline into research can further elucidate the role of α-Syn in disease progression.
The Neurodex biomarker pipeline ensures that α-Synuclein’s role in disease is monitored effectively.
Adopting the Neurodex biomarker pipeline as a standard can revolutionize the understanding of α-Syn in neurobiology.
This integration of the Neurodex biomarker pipeline is vital for understanding α-Synuclein’s implications in neurodegeneration.
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-kB) is a transcription factor that plays a critical role in regulating immune response and inflammation. Dysregulation of NF-kB signaling is implicated in several neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease and multiple sclerosis. By measuring NF-kB activity, researchers can gain insights into the inflammatory processes contributing to neurodegeneration. Therapeutic strategies targeting NF-kB signaling pathways may hold promise in mitigating neurodegenerative disease progression by addressing underlying inflammatory mechanisms.
In the context of the Neurodex biomarker pipeline, monitoring NF-kB activity can provide critical insights into the inflammatory processes that underlie neurodegenerative diseases.
The implications of the Neurodex biomarker pipeline extend to therapeutic interventions targeting NF-kB signaling.
Utilizing the Neurodex biomarker pipeline allows researchers to target NF-kB for therapeutic advancements.
Advanced insights from the Neurodex biomarker pipeline on NF-kB can inform future therapeutic developments.
Further exploration of NF-kB through the Neurodex biomarker pipeline can lead to innovative treatments.
LC3, or microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3, is essential for autophagy, a cellular process that removes damaged organelles and proteins. In neurodegenerative diseases, impaired autophagy can lead to the accumulation of toxic proteins. Studies have highlighted the significance of LC3 as a biomarker in various neurodegenerative disorders, as its levels can indicate the efficiency of autophagic processes. Understanding LC3 dynamics may offer insights into the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative diseases and guide therapeutic strategies aimed at enhancing autophagy.
The Neurodex biomarker pipeline emphasizes the importance of LC3 as a significant indicator of autophagy dysfunction in neurodegenerative disorders.
The significance of LC3 within the Neurodex biomarker pipeline reinforces its role in autophagy-related neurodegeneration.
The Neurodex biomarker pipeline enhances our understanding of LC3’s function in neurodegenerative disorders.
The Neurodex biomarker pipeline emphasizes the clinical relevance of LC3 in monitoring neurodegenerative conditions.
The significance of LC3 within the Neurodex biomarker pipeline can influence therapeutic strategies.
NFL, or neurofilament light chain, is a structural protein found in neurons that can be released into the CSF during neurodegeneration. Elevated levels of NFL have been associated with various neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease, ALS, and traumatic brain injury. NFL serves as a promising biomarker for monitoring disease progression and therapeutic response. Recent studies suggest that NFL levels in the CSF and blood can be correlated with the severity of neurodegeneration, making it a valuable tool in clinical settings.
The role of NFL in the Neurodex biomarker pipeline highlights its potential as a reliable biomarker for various neurodegenerative diseases.
The Neurodex biomarker pipeline supports the use of NFL as a monitoring tool for neurodegenerative disease progression.
Integrating NFL into the Neurodex biomarker pipeline provides more accurate assessments of neurodegeneration.
Employing NFL within the Neurodex biomarker pipeline is crucial for understanding disease severity.
Highlighting NFL in the Neurodex biomarker pipeline enhances its application in clinical settings.
The Tau protein, particularly its phosphorylated form (pTau), plays a significant role in the development of Alzheimer’s disease. Tau is essential for stabilizing microtubules; however, when hyperphosphorylated, it forms neurofibrillary tangles, contributing to neuronal dysfunction. Measuring pTau levels in the CSF can help in the early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease and differentiate it from other dementias. Furthermore, ongoing studies aim to understand the relationship between pTau levels and cognitive decline, which could pave the way for targeted therapies and interventions.
Within the Neurodex biomarker pipeline, the measurement of pTau levels can facilitate early diagnosis and treatment strategies for Alzheimer’s disease.
The Neurodex biomarker pipeline aims to improve the standardization of pTau measurements in clinical settings.
The Neurodex biomarker pipeline facilitates the assessment of pTau, contributing to better Alzheimer’s diagnostics.
The Neurodex biomarker pipeline aims to clarify the role of pTau in Alzheimer’s disease development.
Understanding pTau’s role via the Neurodex biomarker pipeline is crucial for Alzheimer’s research.
TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) has emerged as another critical player in the pathology of neurodegenerative diseases, particularly amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementia (FTD). TDP-43 is involved in various cellular processes, including RNA metabolism and stress response. Abnormal hyperphosphorylation and aggregation of TDP-43 in neurons are commonly observed in these conditions. Notably, the detection of TDP-43 in the CSF may provide insight into disease progression and help differentiate between various forms of dementia, thereby enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
The detection of TDP-43 levels is a critical aspect of the Neurodex biomarker pipeline, aiding in the differentiation of various neurodegenerative conditions.
Understanding TDP-43 in the framework of the Neurodex biomarker pipeline can enhance diagnostic precision and patient management.
The inclusion of TDP-43 in the Neurodex biomarker pipeline is vital for advancing knowledge in neurodegenerative research.
By incorporating TDP-43 in the Neurodex biomarker pipeline, researchers can enhance diagnostic accuracy.
The Neurodex biomarker pipeline plays a significant role in linking TDP-43 to various neurodegenerative diseases.